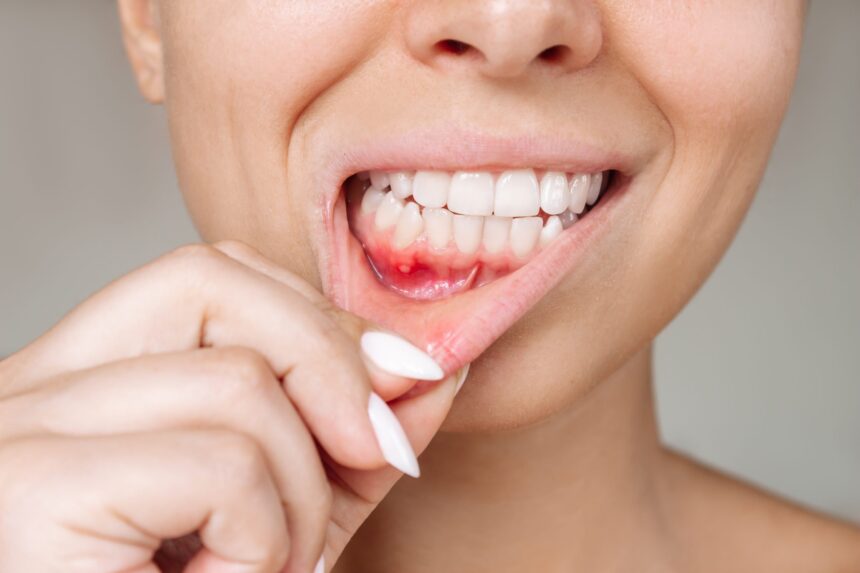
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common but serious oral health condition that affects the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. It often develops slowly and painlessly, which means many people may not realize they have it until significant damage has occurred. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and prevention of gum disease is essential for maintaining healthy teeth, gums, and overall health.
Understanding Gum Disease
Gum disease is an infection of the tissues that surround and support the teeth. It usually begins with mild inflammation and can progress to severe damage if left untreated.
Types of Gum Disease
There are two main stages of gum disease:
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is the early stage of gum disease and is characterized by gum inflammation. At this stage, the condition is reversible with proper oral care.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is an advanced stage where the gums pull away from the teeth, forming pockets that become infected. This stage can lead to tooth loss and bone damage.
Symptoms of Gum Disease
Symptoms may vary depending on the stage of the disease.
Early Symptoms
Common early signs include:
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Bleeding gums during brushing or flossing
- Bad breath that does not go away
These symptoms are often ignored, allowing the disease to progress.
Advanced Symptoms
As gum disease worsens, symptoms may include:
- Receding gums
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Pain while chewing
- Formation of pus between gums and teeth
- Changes in bite alignment
Advanced gum disease requires professional treatment.
Causes of Gum Disease
Gum disease develops due to multiple factors, often related to poor oral hygiene.
Plaque Buildup
The primary cause of gum disease is plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on teeth. If plaque is not removed, it hardens into tartar, which irritates the gums.
Poor Oral Hygiene
Inadequate brushing and flossing allow bacteria to grow, increasing the risk of infection and inflammation.
Lifestyle and Health Factors
Other contributing factors include:
- Smoking and tobacco use
- Poor nutrition
- Diabetes
- Hormonal changes
- Stress
- Weakened immune system
These factors increase susceptibility to gum disease.
Health Risks Associated With Gum Disease
Untreated gum disease can affect more than just oral health.
Impact on Teeth and Jawbone
Gum disease can cause:
- Tooth loss
- Bone deterioration
- Weakening of tooth support structures
Effects on Overall Health
Research shows links between gum disease and:
- Heart disease
- Diabetes complications
- Respiratory infections
Maintaining gum health is important for overall well-being.
Diagnosis of Gum Disease
Early diagnosis helps prevent serious complications.
Dental Examination
Dentists diagnose gum disease by:
- Examining gums for inflammation and recession
- Measuring pocket depth around teeth
- Reviewing dental X-rays
Regular dental visits help detect gum disease early.
Prevention of Gum Disease
Gum disease is largely preventable with good oral care habits.
Daily Oral Hygiene Practices
Effective prevention includes:
- Brushing teeth twice daily
- Flossing once a day
- Using antibacterial mouthwash
These practices help remove plaque and bacteria.
Importance of Regular Dental Checkups
Professional cleanings remove tartar that brushing cannot. Regular checkups also help identify early signs of gum disease.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
To protect gum health:
- Avoid smoking
- Eat a balanced diet
- Manage stress
- Control medical conditions like diabetes
Healthy habits strengthen gums and immune response.
Treatment Options for Gum Disease
Treatment depends on the severity of the condition.
Treatment for Early-Stage Gum Disease
Gingivitis can often be treated with:
- Improved oral hygiene
- Professional dental cleaning
Treatment for Advanced Gum Disease
Severe cases may require:
- Deep cleaning procedures
- Medications
- Surgical treatment
Early treatment improves outcomes and prevents tooth loss.
Conclusion
Gum disease is a common but preventable condition that can have serious consequences if ignored. Recognizing early symptoms, understanding the causes, and practicing effective prevention strategies are key to maintaining healthy gums and teeth. Good oral hygiene, regular dental checkups, and healthy lifestyle choices play a crucial role in preventing gum disease. By taking proactive steps, individuals can protect their oral health and support their overall well-being for a lifetime.